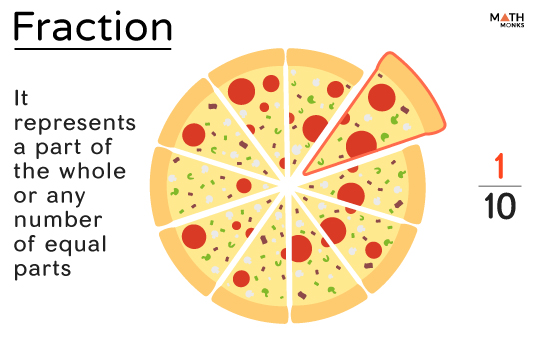
Fractions represent a part of the whole. It represents the number of parts of a certain number, size, or collection compared to the total number of equal parts.
A number is written in the fractional form as $>$
If a pizza is cut into ten equal slices and one slice of the pizza is placed on a dish, then each dish is said to have $>$ of the pizza. It is read as ‘one-tenth’ or ‘1 by 10.’

Here are some more real-life examples involving fractions:
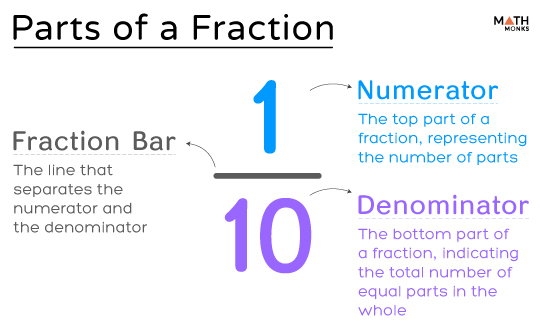
A fraction consists of two main parts: a numerator and a denominator, separated by a horizontal bar known as the fraction bar.
The numerator is the top number above the fraction bar, indicating how many parts we have.
The denominator is the number below the fraction bar, which shows how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
The diagram below shows the different parts of the fraction $>$.
A fraction can be represented in three ways: a fraction, a percentage, or a decimal.
It is the most common form of representing fractions. A fraction in fractional form is denoted in $>$ form, where p is the numerator, q is the denominator, and they are separated by a fraction bar.
Example
$>$ represents 1 part out of 10 equal parts of a whole. Here, the numerator is 1, and the denominator is 10
In this form, the fraction is represented as a decimal number.
Example
The fraction $>$ can be written in decimal form by dividing the numerator (1) by the denominator (10), which gives 0.1
The fraction can also be represented as a percentage by multiplying the fraction by 100.
Example
The fraction $>$ is multiplied by 100
Thus, $>$ is percentage form is 10%
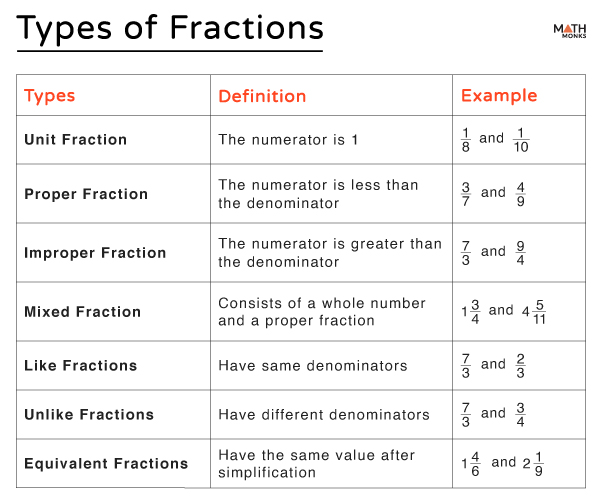
Fractions can be classified into several types:
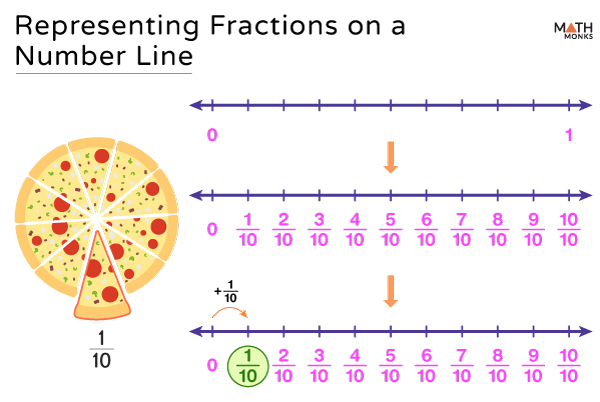
A number line is a useful tool for visualizing fractions. Let us express $>$ on the number line.
Here is the number line.
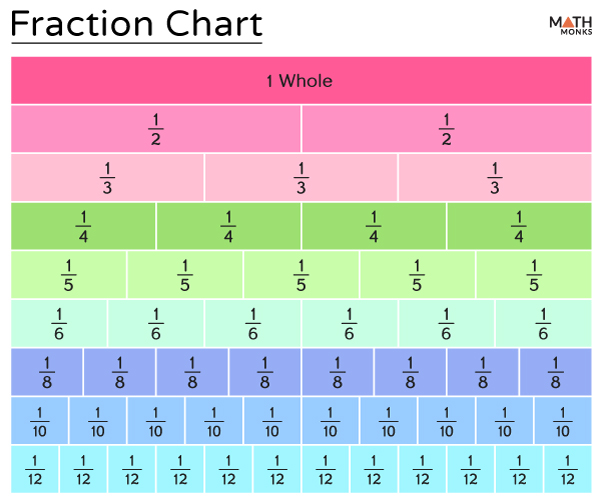
Here is a printable chart for visualizing equivalent fractions.
Here are some properties used to simplify problems involving fractions.
Simplifying a fraction means to reduce the fraction to its simplest form. To simplify, we divide the numerator and denominator by the greatest common factor (GCF).
The GCF of 20 and 30 is 10
Now, by dividing the numerator and denominator by 10, we get
To add or subtract fractions with the same denominator, we follow the following steps:
Step 1: Adding/subtracting the numerators together
Step 2: Simplifying
Now, if we subtract the fraction $>$ from $>$, then
We follow the given steps to add or subtract fractions with different denominators.
Step 1: Finding the LCM of the denominators
Here, the denominators are 2 and 4
The LCM of 2 and 4 is 4
Step 2: Rationalizing the denominators
Now, for rationalizing, we will multiply the first fraction by 2 and the second fraction by 1
= $+\dfrac>$, the fractions with the same denominators.
Step 3: Adding the numerators together
Step 4: Simplifying
While multiplying fractions, we multiply all the numerators and all the denominators together.
While dividing the fractions, we multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
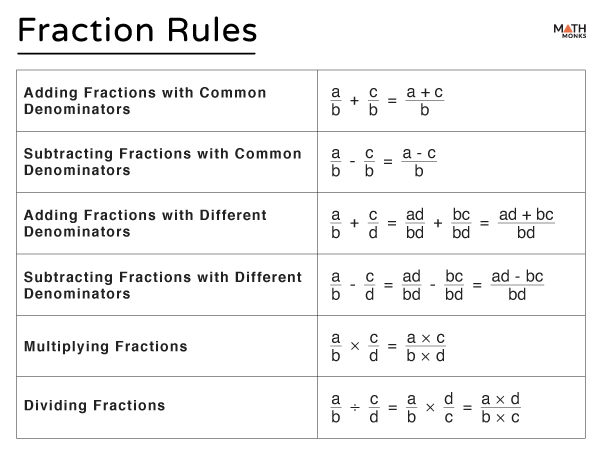
Here is a summary of the rules we follow for simplifying fractions.
In a class of 60 students, $>$ of them went on a family trip during their summer break. How many students went on a trip?
Here, the total number of students is 60
As we know,
The number of students who went on a family trip is $>$ of the total number of students.
Thus, the number of students who went on a trip
= $>$ of 60
= $\times 60>$
= $$
Last modified on August 22nd, 2024